Bone Classification
Bones can be classified into four main categories based on their shapes: long, short, flat, and irregular. Long bones, such as the femur, are characterized by a greater length than width and are primarily involved in movement. Short bones, like the carpals, are roughly cube-shaped and provide stability and support. Flat bones, such as the skull, serve protective functions, while irregular bones, like the vertebrae, have complex shapes that fulfill various roles.
Recommended video:
Structural Joint Classifications
Long Bones
Long bones are elongated structures that are crucial for movement and support. They consist of a diaphysis (shaft) and epiphyses (ends), and they contain a medullary cavity filled with bone marrow. Examples include the humerus and tibia. Their design allows for leverage and weight-bearing, making them essential in the skeletal system.
Recommended video:
Flat Bones
Flat bones are thin, flattened structures that primarily serve protective roles and provide surfaces for muscle attachment. They are typically composed of two layers of compact bone surrounding a layer of spongy bone. Examples include the sternum and ribs. Their shape allows them to shield vital organs and contribute to the overall structure of the body.
Recommended video:
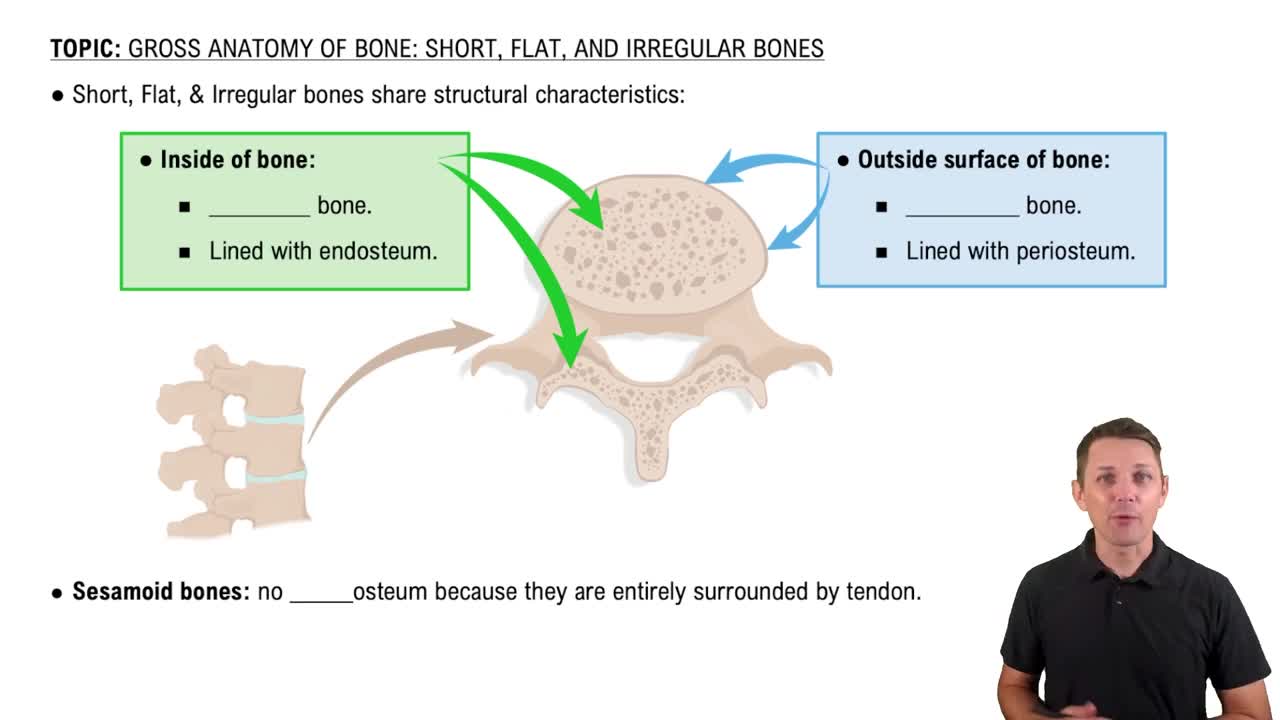
Short, Flat, and Irregular Bones
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 2:58m
2:58m