Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Osteocyte
Osteocytes are mature bone cells that originate from osteoblasts, which are responsible for bone formation. They reside in small cavities called lacunae within the bone matrix and play a crucial role in maintaining bone tissue. Osteocytes communicate with other bone cells through long, hair-like extensions called dendritic processes, allowing them to regulate bone remodeling and mineral homeostasis.
Recommended video:
Bone Remodeling
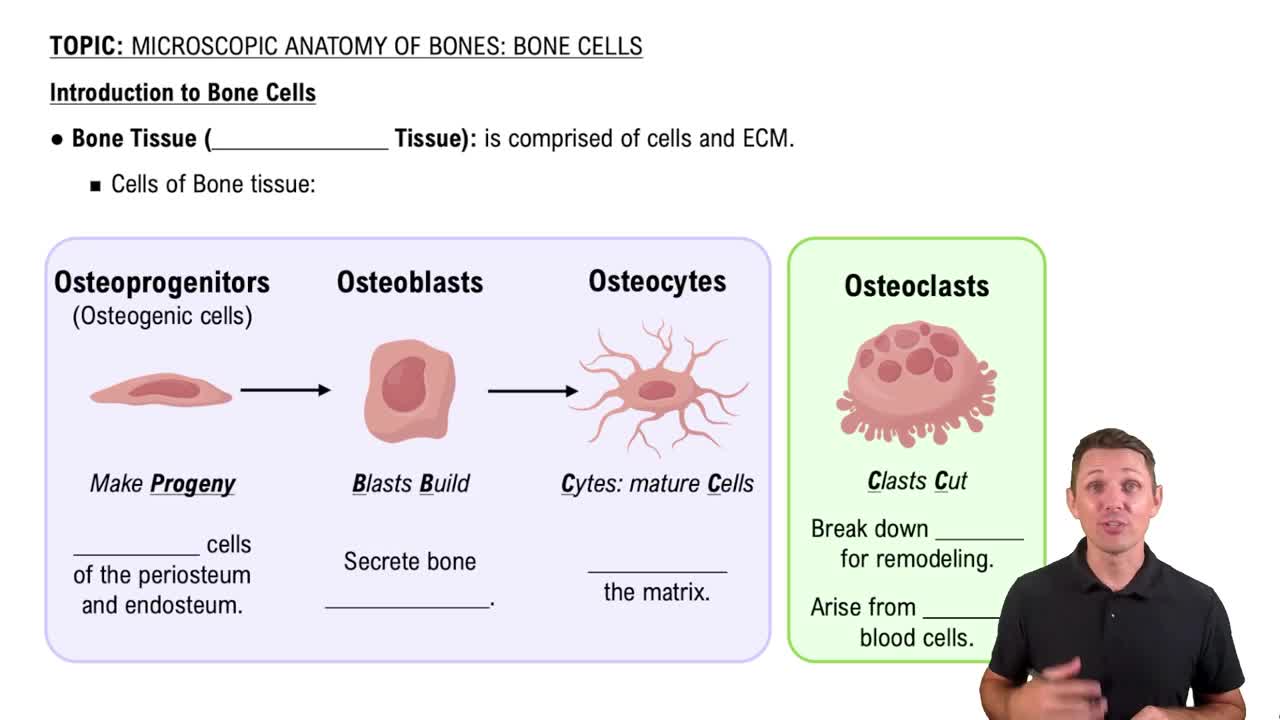
Bone remodeling is a continuous process where old bone tissue is replaced by new bone tissue. This process involves the coordinated activity of osteoclasts (cells that break down bone) and osteoblasts (cells that build bone). Osteocytes, as the most abundant bone cells, help regulate this process by sensing mechanical stress and signaling the need for bone formation or resorption.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Bone Cells
Bone Matrix
The bone matrix is the extracellular component of bone tissue, composed of organic and inorganic materials. The organic part mainly consists of collagen fibers, which provide tensile strength, while the inorganic part is primarily hydroxyapatite, a mineral that gives bone its hardness. The matrix serves as a scaffold for osteocytes and is essential for the overall structural integrity and function of bones.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution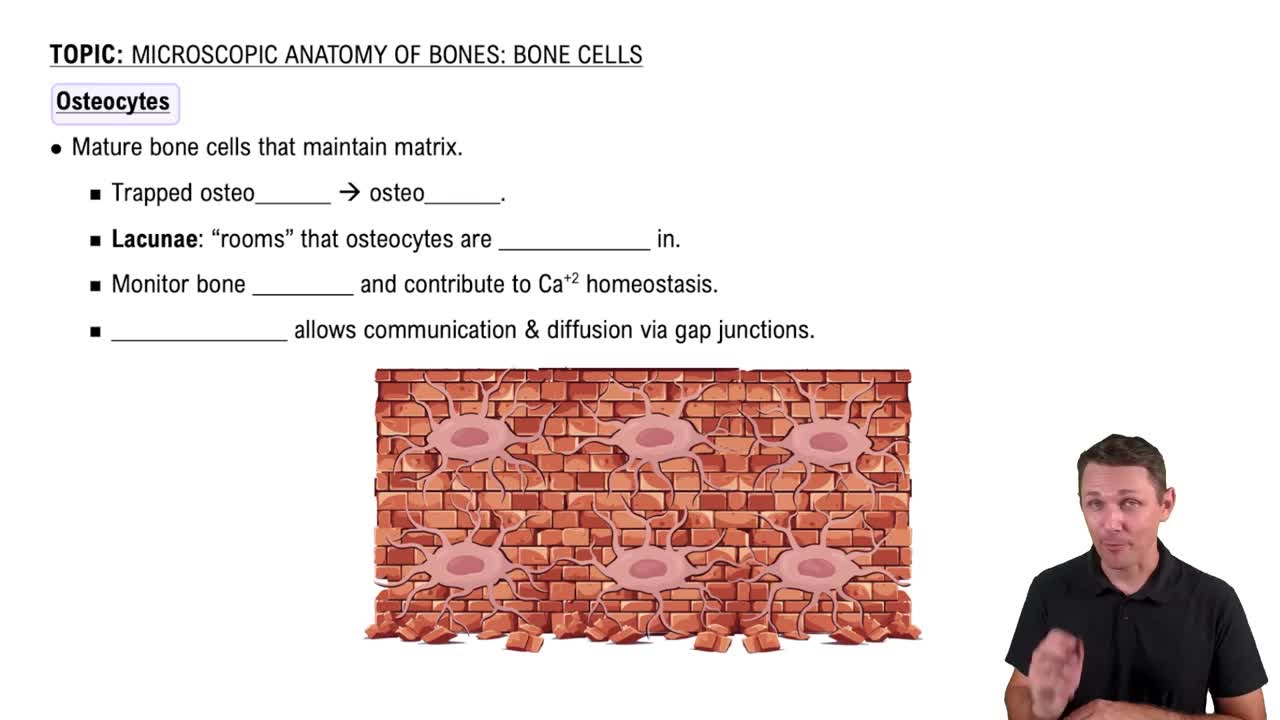


 4:19m
4:19m