Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Endosymbiosis Theory
The endosymbiosis theory posits that certain organelles, particularly mitochondria and chloroplasts, originated from free-living prokaryotic organisms that were engulfed by ancestral eukaryotic cells. This theory explains the evolutionary relationship between eukaryotes and prokaryotes, suggesting that these organelles retained their own DNA and functions after being incorporated into host cells.
Recommended video:
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)
Mitochondrial DNA is the genetic material found in mitochondria, distinct from the nuclear DNA located in the cell nucleus. It is inherited maternally and is circular in structure, similar to bacterial DNA. The presence of mtDNA supports the idea that mitochondria evolved from ancestral bacteria, reinforcing the endosymbiosis theory.
Recommended video:
Phylogenetic Evidence
Phylogenetic evidence involves analyzing the evolutionary relationships between different organisms based on genetic data. The close relationship between mitochondrial DNA and bacterial DNA, particularly in terms of sequence similarity and structure, provides strong phylogenetic support for the endosymbiosis theory, indicating that mitochondria share a common ancestor with certain bacteria.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution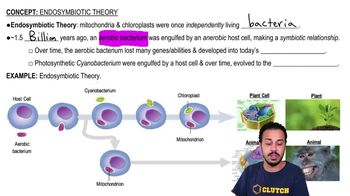



 6:58m
6:58m