Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
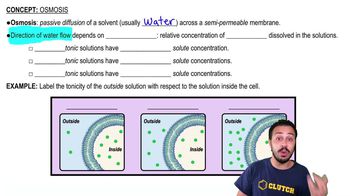
Osmosis
Osmosis is the movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration. This process is crucial for maintaining cell homeostasis and is driven by the concentration gradient of solutes. In a hypotonic solution, the concentration of solutes outside the cell is lower than inside, prompting water to move into the cell.
Recommended video:
Hypotonic Solution
A hypotonic solution has a lower concentration of solutes compared to the inside of a cell. When a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, water enters the cell to balance the solute concentrations, which can lead to cell swelling and potentially bursting if the influx of water is excessive. Understanding this concept is essential for predicting the behavior of cells in different osmotic environments.
Recommended video:
Homogenous vs. Heterogenous Solutions
Net Movement of Water
The net movement of water refers to the overall direction of water flow when considering both the influx and efflux of water molecules. In a hypotonic environment, while water may move in and out of the cell, the net movement will be into the cell due to the higher internal solute concentration. This concept helps in understanding the dynamic equilibrium that cells strive to achieve in response to osmotic pressures.
Recommended video: