Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
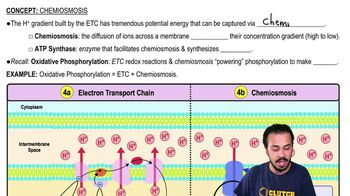
Chemiosmosis
Chemiosmosis is the process by which ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is produced in cells through the movement of protons (H+) across a membrane. In mitochondria, this occurs when protons are pumped into the intermembrane space, creating a gradient that drives ATP synthesis as protons flow back into the mitochondrial matrix. DNP disrupts this process by making the inner mitochondrial membrane permeable to protons, preventing efficient ATP production.
Recommended video:
Thermogenesis
Thermogenesis refers to the process of heat production in organisms, particularly in response to energy expenditure. When DNP uncouples oxidative phosphorylation, the energy that would normally be used to produce ATP is released as heat instead. This results in increased body temperature and profuse sweating as the body attempts to dissipate the excess heat, contributing to weight loss through elevated metabolic rates.
Toxicity and Metabolic Disruption
The use of DNP can lead to severe toxicity due to its ability to disrupt normal metabolic processes. By uncoupling oxidative phosphorylation, DNP causes cells to burn through energy reserves rapidly, leading to a state of hypermetabolism. This can result in dangerous side effects, including hyperthermia, dehydration, and ultimately, death, as the body cannot maintain homeostasis under such extreme conditions.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Metabolism