Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Bone Tissue Composition
Bone tissue is composed of both organic and inorganic components. The organic matrix, primarily collagen fibers, provides flexibility and tensile strength, while the inorganic matrix, mainly hydroxyapatite, contributes to the rigidity and compressive strength of bones. Understanding this dual composition is essential for evaluating the statements about bone strength.
Recommended video:
Specialized Connective Tissue: Bone Example 1
Role of Collagen in Bone
Collagen is a crucial protein in the organic matrix of bone tissue, providing structural support and flexibility. It helps bones withstand tensile forces and prevents fractures. Recognizing the importance of collagen alongside the inorganic components is vital for accurately assessing the strength of bone tissue.
Recommended video:
Bone Remodeling
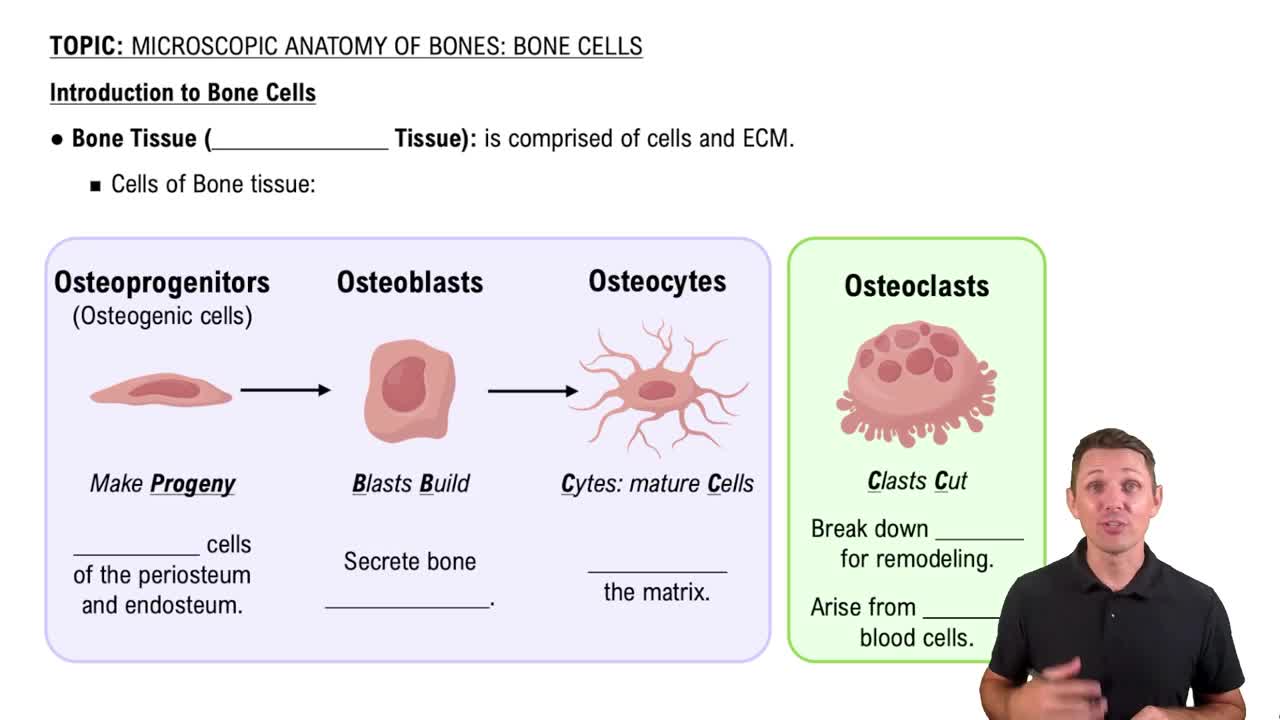
Bone remodeling is a continuous process where old bone tissue is replaced by new bone tissue, involving the activities of osteoblasts (bone-forming cells) and osteoclasts (bone-resorbing cells). This process is essential for maintaining bone strength and integrity, highlighting that bone strength is not solely dependent on the inorganic matrix.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Bone Cells
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution