Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Electronegativity
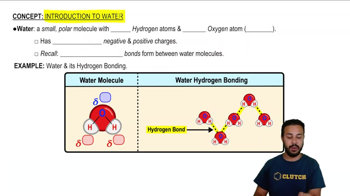
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract and hold onto electrons in a chemical bond. In the case of water (H2O), oxygen is significantly more electronegative than hydrogen, leading to polar covalent bonds. This polarity creates a dipole moment, resulting in unique properties of water, such as high surface tension and solvent capabilities.
Recommended video:
Polarity of Water
The polarity of water arises from the unequal sharing of electrons between oxygen and hydrogen due to the difference in electronegativity. This polarity allows water molecules to form hydrogen bonds with each other, contributing to its high boiling point, specific heat capacity, and solvent properties. If oxygen and hydrogen had equal electronegativity, water would be nonpolar, drastically altering these properties.
Recommended video:
Hydrogen Bonding
Hydrogen bonding is a type of weak chemical bond that occurs when a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a highly electronegative atom, like oxygen, experiences an attraction to another electronegative atom. In water, these bonds are responsible for many of its unique physical properties, including its high boiling point and ability to dissolve many substances. Equal electronegativity would eliminate hydrogen bonding, leading to a significant change in water's behavior and characteristics.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 5:19m
5:19m