Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Phototransduction
Phototransduction is the process by which light is converted into electrical signals in the retina. In darkness, photoreceptor cells (rods and cones) are depolarized due to the continuous influx of sodium ions, leading to the release of neurotransmitters that inhibit bipolar cells. Understanding this process is crucial for grasping how visual signals are initiated.
Recommended video:
Rods and Cones
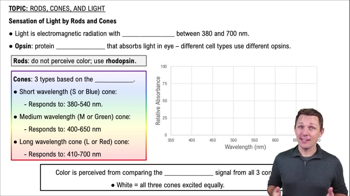
Rods and cones are the two types of photoreceptor cells in the retina. Rods are highly sensitive to light and enable vision in low-light conditions, while cones are responsible for color vision and function best in bright light. In darkness, rods are primarily active and contribute to the depolarization of the retinal cells.
Recommended video:
Sensation of Light by Rods and Cones
Retinal Processing
Retinal processing refers to the way visual information is processed by various types of retinal cells, including bipolar and ganglion cells. In the dark, the depolarization of rods and cones leads to a cascade of inhibitory signals that affect bipolar cells, ultimately influencing the output of ganglion cells. This concept is essential for understanding how visual signals are transmitted to the brain.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 5:4m
5:4m