Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Anatomy & Physiology5h 40m
- What is Anatomy & Physiology?20m
- Levels of Organization13m
- Variation in Anatomy & Physiology12m
- Introduction to Organ Systems27m
- Homeostasis9m
- Feedback Loops11m
- Feedback Loops: Negative Feedback19m
- Feedback Loops: Positive Feedback11m
- Anatomical Position7m
- Introduction to Directional Terms3m
- Directional Terms: Up and Down9m
- Directional Terms: Front and Back6m
- Directional Terms: Body Sides12m
- Directional Terms: Limbs6m
- Directional Terms: Depth Within the Body4m
- Introduction to Anatomical Terms for Body Regions3m
- Anatomical Terms for the Head and Neck8m
- Anatomical Terms for the Front of the Trunk8m
- Anatomical Terms for the Back9m
- Anatomical Terms for the Arm and Hand9m
- Anatomical Terms for the Leg and Foot15m
- Review- Using Anatomical Terms and Directions12m
- Abdominopelvic Quadrants and Regions19m
- Anatomical Planes & Sections17m
- Organization of the Body: Body Cavities13m
- Organization of the Body: Serous Membranes14m
- Organization of the Body: Serous Membrane Locations8m
- Organization of the Body: Thoracic Cavity8m
- Organization of the Body: Abdominopelvic Cavity12m
- 2. Cell Chemistry & Cell Components12h 37m
- Atoms- Smallest Unit of Matter57m
- Isotopes39m
- Introduction to Chemical Bonding19m
- Covalent Bonds40m
- Noncovalent Bonds5m
- Ionic Bonding37m
- Hydrogen Bonding19m
- Introduction to Water7m
- Properties of Water- Cohesion and Adhesion7m
- Properties of Water- Density8m
- Properties of Water- Thermal14m
- Properties of Water- The Universal Solvent17m
- Acids and Bases12m
- pH Scale21m
- Carbon8m
- Functional Groups9m
- Introduction to Biomolecules2m
- Monomers & Polymers11m
- Carbohydrates23m
- Proteins25m
- Nucleic Acids34m
- Lipids28m
- Microscopes10m
- Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells26m
- Introduction to Eukaryotic Organelles16m
- Endomembrane System: Protein Secretion34m
- Endomembrane System: Digestive Organelles15m
- Mitochondria & Chloroplasts21m
- Endosymbiotic Theory10m
- Introduction to the Cytoskeleton10m
- Cell Junctions8m
- Biological Membranes10m
- Types of Membrane Proteins7m
- Concentration Gradients and Diffusion9m
- Introduction to Membrane Transport14m
- Passive vs. Active Transport13m
- Osmosis33m
- Simple and Facilitated Diffusion17m
- Active Transport30m
- Endocytosis and Exocytosis15m
- 3. Energy & Cell Processes10h 7m
- Introduction to Energy15m
- Laws of Thermodynamics15m
- Chemical Reactions9m
- ATP20m
- Enzymes14m
- Enzyme Activation Energy9m
- Enzyme Binding Factors9m
- Enzyme Inhibition10m
- Introduction to Metabolism8m
- Redox Reactions15m
- Introduction to Cellular Respiration22m
- Types of Phosphorylation11m
- Glycolysis19m
- Pyruvate Oxidation8m
- Krebs Cycle16m
- Electron Transport Chain14m
- Chemiosmosis7m
- Review of Aerobic Cellular Respiration19m
- Fermentation & Anaerobic Respiration23m
- Introduction to Cell Division22m
- Organization of DNA in the Cell17m
- Introduction to the Cell Cycle7m
- Interphase18m
- Phases of Mitosis48m
- Cytokinesis16m
- Cell Cycle Regulation18m
- Review of the Cell Cycle7m
- Cancer13m
- Introduction to DNA Replication22m
- DNA Repair7m
- Central Dogma7m
- Introduction to Transcription20m
- Steps of Transcription19m
- Genetic Code25m
- Introduction to Translation30m
- Steps of Translation23m
- Post-Translational Modification6m
- 4. Tissues & Histology10h 3m
- Introduction to Tissues & Histology16m
- Introduction to Epithelial Tissue24m
- Characteristics of Epithelial Tissue37m
- Structural Naming of Epithelial Tissue19m
- Simple Epithelial Tissues1h 2m
- Stratified Epithelial Tissues55m
- Identifying Types of Epithelial Tissue32m
- Glandular Epithelial Tissue26m
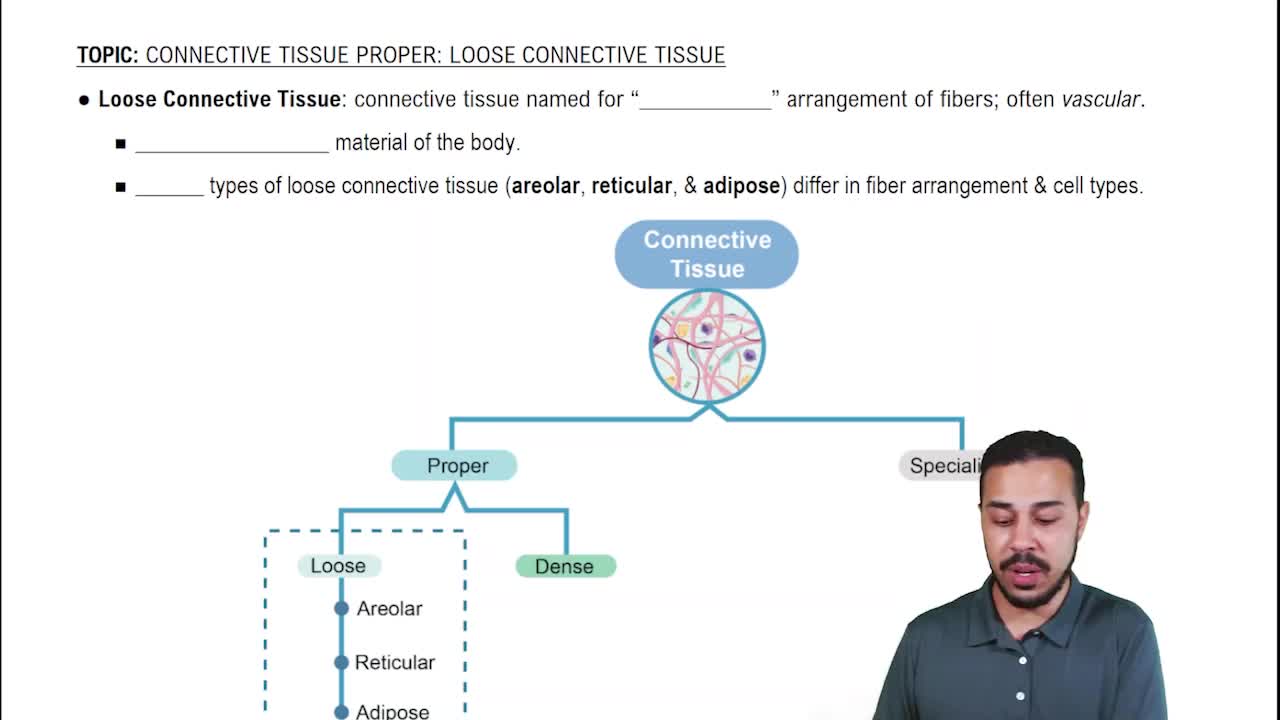
- Introduction to Connective Tissue36m
- Classes of Connective Tissue8m
- Introduction to Connective Tissue Proper40m
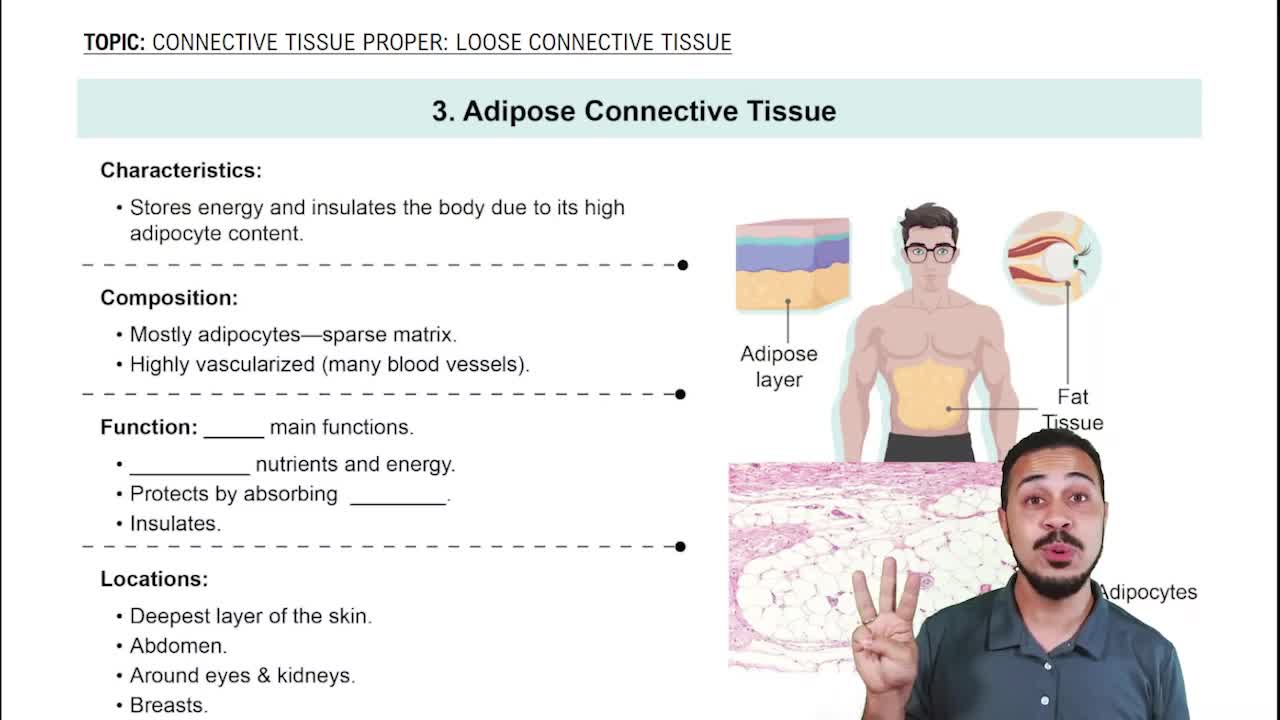
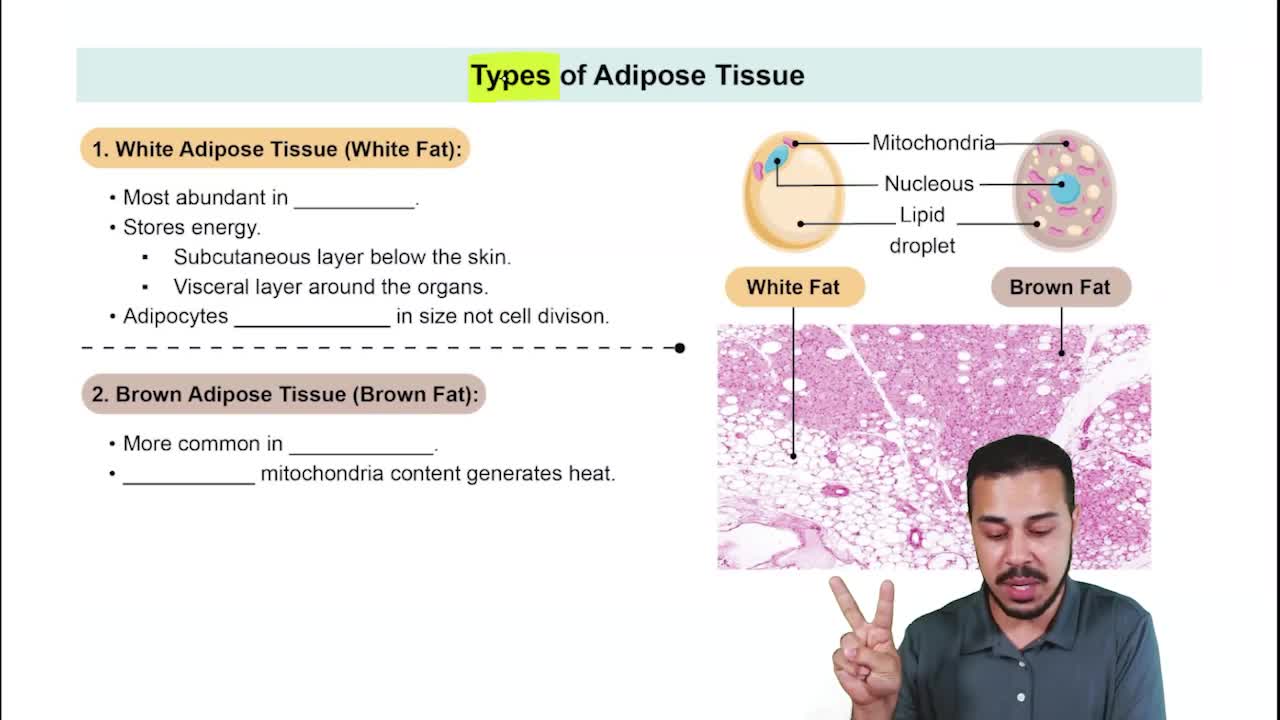
- Connective Tissue Proper: Loose Connective Tissue56m
- Connective Tissue Proper: Dense Connective Tissue49m
- Specialized Connective Tissue: Cartilage44m
- Specialized Connective Tissue: Bone12m
- Specialized Connective Tissue: Blood9m
- Introduction to Muscle Tissue7m
- Types of Muscle Tissue45m
- Introduction to Nervous Tissue8m
- Nervous Tissue: The Neuron8m
- 5. Integumentary System2h 20m
- 6. Bones & Skeletal Tissue2h 16m
- An Introduction to Bone and Skeletal Tissue18m
- Gross Anatomy of Bone: Compact and Spongy Bone7m
- Gross Anatomy of Bone: Periosteum and Endosteum11m
- Gross Anatomy of Bone: Bone Marrow8m
- Gross Anatomy of Bone: Short, Flat, and Irregular Bones5m
- Gross Anatomy of Bones - Structure of a Long Bone23m
- Microscopic Anatomy of Bones - Bone Matrix9m
- Microscopic Anatomy of Bones - Bone Cells25m
- Microscopic Anatomy of Bones - The Osteon17m
- Microscopic Anatomy of Bones - Trabeculae9m
- 7. The Skeletal System2h 35m
- 8. Joints2h 17m
- 9. Muscle Tissue2h 33m
- 10. Muscles1h 11m
- 11. Nervous Tissue and Nervous System1h 35m
- 12. The Central Nervous System1h 6m
- 13. The Peripheral Nervous System1h 26m
- Introduction to the Peripheral Nervous System5m
- Organization of Sensory Pathways16m
- Introduction to Sensory Receptors5m
- Sensory Receptor Classification by Modality6m
- Sensory Receptor Classification by Location8m
- Proprioceptors7m
- Adaptation of Sensory Receptors8m
- Introduction to Reflex Arcs13m
- Reflex Arcs15m
- 14. The Autonomic Nervous System1h 38m
- 15. The Special Senses2h 41m
- 16. The Endocrine System2h 48m
- 17. The Blood1h 22m
- 18. The Heart1h 42m
- 19. The Blood Vessels3h 35m
- 20. The Lymphatic System3h 16m
- 21. The Immune System14h 37m
- Introduction to the Immune System10m
- Introduction to Innate Immunity17m
- Introduction to First-Line Defenses5m
- Physical Barriers in First-Line Defenses: Skin13m
- Physical Barriers in First-Line Defenses: Mucous Membrane9m
- First-Line Defenses: Chemical Barriers24m
- First-Line Defenses: Normal Microbiota7m
- Introduction to Cells of the Immune System15m
- Cells of the Immune System: Granulocytes28m
- Cells of the Immune System: Agranulocytes26m
- Introduction to Cell Communication5m
- Cell Communication: Surface Receptors & Adhesion Molecules16m
- Cell Communication: Cytokines27m
- Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs)48m
- Introduction to the Complement System24m
- Activation Pathways of the Complement System23m
- Effects of the Complement System23m
- Review of the Complement System13m
- Phagocytosis17m
- Introduction to Inflammation18m
- Steps of the Inflammatory Response28m
- Fever8m
- Interferon Response25m
- Review Map of Innate Immunity
- Introduction to Adaptive Immunity32m
- Antigens12m
- Introduction to T Lymphocytes38m
- Major Histocompatibility Complex Molecules20m
- Activation of T Lymphocytes21m
- Functions of T Lymphocytes25m
- Review of Cytotoxic vs Helper T Cells13m
- Introduction to B Lymphocytes27m
- Antibodies14m
- Classes of Antibodies35m
- Outcomes of Antibody Binding to Antigen15m
- T Dependent & T Independent Antigens21m
- Clonal Selection20m
- Antibody Class Switching17m
- Affinity Maturation14m
- Primary and Secondary Response of Adaptive Immunity21m
- Immune Tolerance28m
- Regulatory T Cells10m
- Natural Killer Cells16m
- Review of Adaptive Immunity25m
- 22. The Respiratory System3h 20m
- 23. The Digestive System2h 5m
- 24. Metabolism and Nutrition4h 0m
- Essential Amino Acids5m
- Lipid Vitamins19m
- Cellular Respiration: Redox Reactions15m
- Introduction to Cellular Respiration22m
- Cellular Respiration: Types of Phosphorylation14m
- Cellular Respiration: Glycolysis19m
- Cellular Respiration: Pyruvate Oxidation8m
- Cellular Respiration: Krebs Cycle16m
- Cellular Respiration: Electron Transport Chain14m
- Cellular Respiration: Chemiosmosis7m
- Review of Aerobic Cellular Respiration18m
- Fermentation & Anaerobic Respiration23m
- Gluconeogenesis16m
- Fatty Acid Oxidation20m
- Amino Acid Oxidation17m
- 25. The Urinary System2h 39m
- 26. Fluid and Electrolyte Balance, Acid Base Balance Coming soon
- 27. The Reproductive System2h 5m
- 28. Human Development1h 21m
- 29. Heredity Coming soon
4. Tissues & Histology
Connective Tissue Proper: Loose Connective Tissue
Problem 4.3c
Textbook Question
Describe the roles of each of the following components of the ECM:
c. Reticular fibers
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Reticular fibers are a type of fiber in the extracellular matrix (ECM) that provide structural support to tissues.
These fibers are composed of type III collagen, which forms a delicate network that supports the cellular components of various tissues.
Reticular fibers are particularly abundant in lymphoid organs such as the spleen, lymph nodes, and bone marrow, where they create a supportive meshwork for immune cells.
They also play a role in the basement membrane, contributing to the filtration function in organs like the kidney.
Overall, reticular fibers help maintain the structural integrity and organization of tissues, facilitating cell attachment and communication.
Recommended similar problem, with video answer:
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
0m:0sPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is a complex network of proteins and carbohydrates that provides structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells. It plays a crucial role in tissue and organ function, influencing cell behavior, migration, and differentiation. Understanding the ECM is essential for comprehending how various components, including reticular fibers, contribute to tissue integrity and function.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Bone Matrix
Reticular Fibers
Reticular fibers are a type of connective tissue fiber composed mainly of collagen type III. They form a delicate, supportive network that helps maintain the structure of organs, particularly in lymphoid tissues and the liver. Their role is vital in providing a scaffold for cells, facilitating the organization of tissues, and supporting the overall architecture of the ECM.
Recommended video:
Guided course
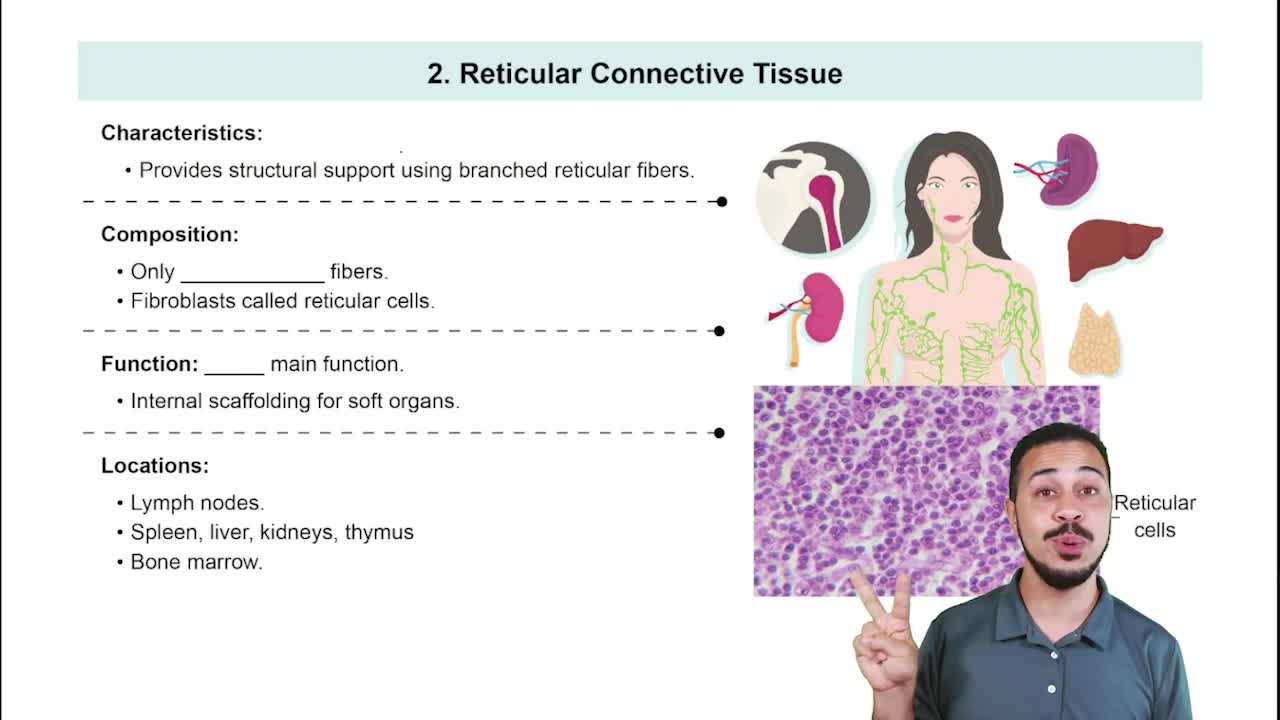
Reticular Connective Tissue
Tissue Support and Organization
The organization and support provided by the ECM, including reticular fibers, are critical for maintaining tissue integrity and function. These fibers help anchor cells in place, allowing for proper communication and nutrient exchange. This structural support is essential for the overall health of tissues, influencing processes such as wound healing and tissue regeneration.
Recommended video:
Guided course
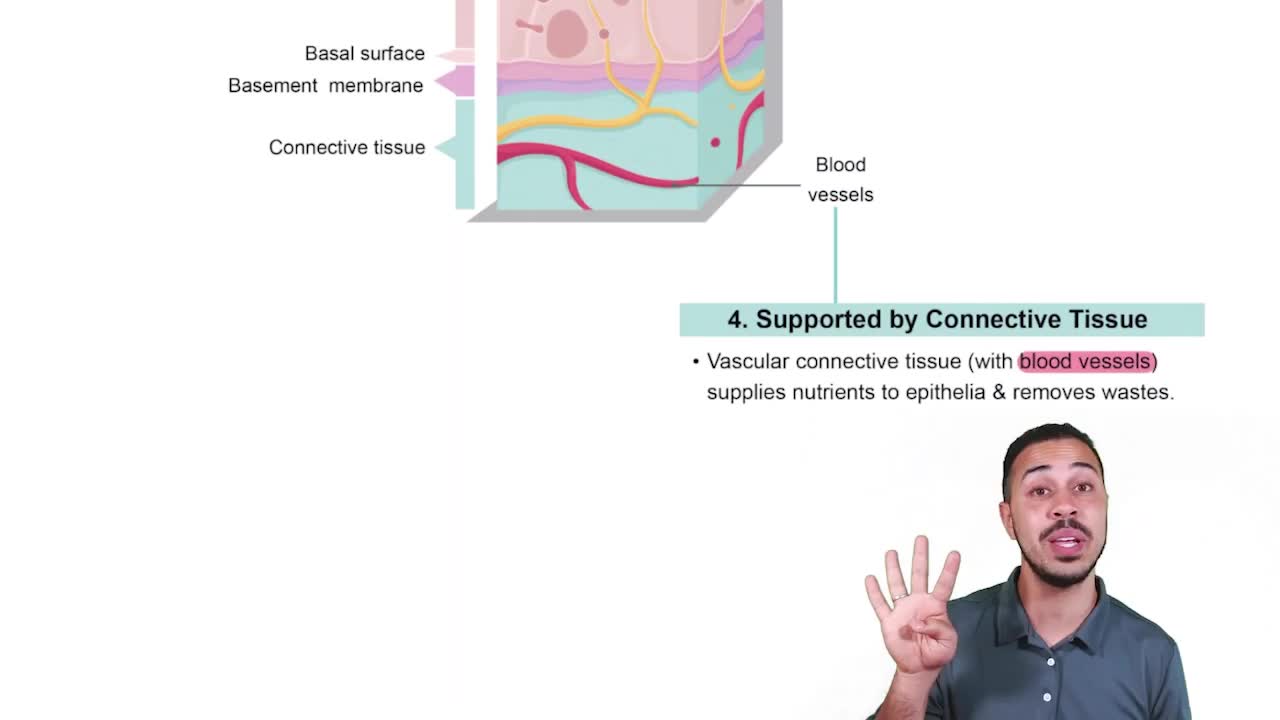
Characteristic 4: Supported by Connective Tissue

 2:46m
2:46mWatch next
Master Loose Connective Tissue with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice