Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Buffer Systems
Buffer systems in the body are chemical solutions that resist changes in pH when acids or bases are added. They work by neutralizing excess hydrogen ions (H+) or hydroxide ions (OH-), maintaining a stable pH in body fluids. Common buffers include bicarbonate, phosphate, and proteins, which play crucial roles in physiological processes.
Recommended video:
pH Regulation
pH regulation is essential for maintaining homeostasis in the body, as enzymes and biochemical reactions are highly sensitive to pH changes. When the pH of body fluids increases (becomes more alkaline), buffer systems help to restore balance by releasing H+ ions to lower the pH back to normal levels, ensuring optimal functioning of cellular processes.
Recommended video:
Feedback Loops
Feedback loops are mechanisms that regulate physiological processes. A negative feedback loop counteracts changes to maintain stability, while a positive feedback loop amplifies changes. In the case of increased pH, the buffer system operates as a negative feedback loop, as it works to counteract the rise in pH and restore equilibrium in the body's internal environment.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Feedback Loops
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution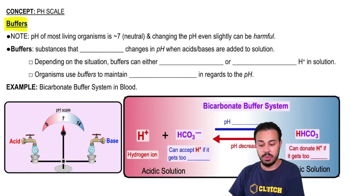



 7:58m
7:58m