Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial tissue consists of sheets of tightly packed cells with minimal extracellular matrix (ECM). It serves as a protective barrier and is involved in absorption, secretion, and sensation. This type of tissue lines surfaces and cavities throughout the body, including the skin and the lining of organs.
Recommended video:
Functions of Epithelial Tissue
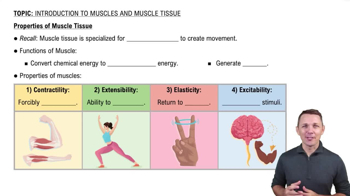
Muscle Tissue
Muscle tissue is composed of excitable cells that are specialized for contraction, enabling movement. There are three types of muscle tissue: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth, each with distinct structures and functions. Skeletal muscle is striated and under voluntary control, while cardiac and smooth muscle are involuntary.
Recommended video:
Properties of Muscle Tissue
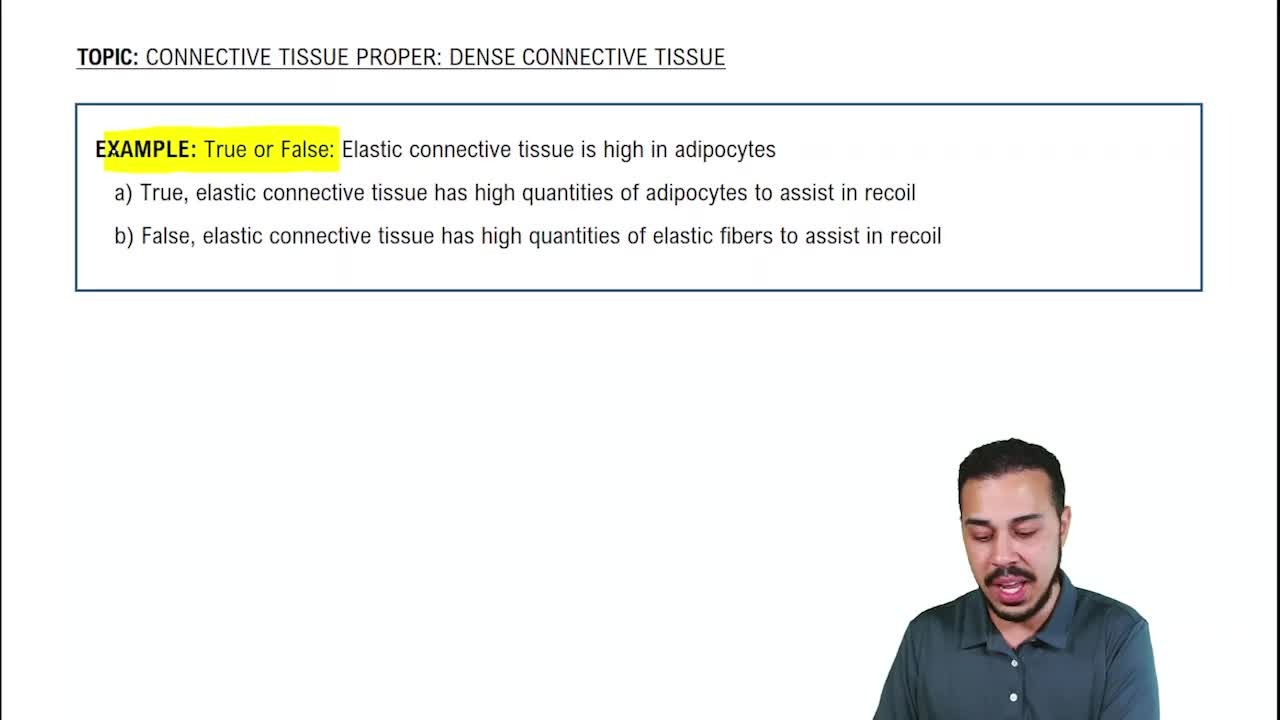
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is characterized by a significant amount of extracellular matrix, which provides structural support and binds other tissues together. It includes various types such as bone, blood, and adipose tissue, and plays crucial roles in support, protection, and transportation of substances throughout the body.
Recommended video:
Connective Tissue Proper: Dense Connective Tissue Example 3