Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose into pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP and NADH in the process. It occurs in the cytoplasm of cells and is the first step in both fermentation and cellular respiration, making it a common pathway for energy extraction from glucose.
Recommended video:
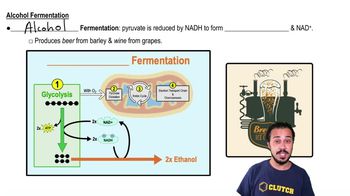
Fermentation
Fermentation is an anaerobic process that allows cells to generate energy without oxygen. It follows glycolysis when oxygen is scarce, converting pyruvate into various end products, such as lactate or ethanol, while regenerating NAD+ to sustain glycolysis and ATP production.
Recommended video:
Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is an aerobic process that fully oxidizes glucose to produce ATP, carbon dioxide, and water. It includes glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain, allowing for a more efficient energy yield compared to fermentation, which only partially oxidizes glucose.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Cellular Respiration