Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Oxidizing Agent
An oxidizing agent is a substance that gains electrons in a chemical reaction, causing another substance to be oxidized. In redox reactions, the oxidizing agent is reduced while facilitating the oxidation of another reactant. Identifying the oxidizing agent is crucial for understanding electron transfer processes in biochemical reactions.
Recommended video:
Redox Reactions
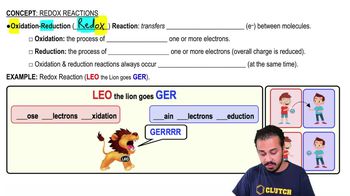
Redox reactions, short for reduction-oxidation reactions, involve the transfer of electrons between two species. One species is oxidized (loses electrons) while the other is reduced (gains electrons). In the context of cellular metabolism, these reactions are vital for energy production and are often coupled with metabolic pathways like glycolysis and fermentation.
Recommended video:
NADH and NAD+
NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) is a reduced form of NAD+, a coenzyme involved in redox reactions. NADH acts as an electron donor, while NAD+ serves as an electron acceptor. In the given reaction, the conversion of pyruvate to lactate involves the reduction of NAD+ to NADH, highlighting the role of these coenzymes in metabolic processes.
Recommended video:
Electron Carriers: NADH & FADH2