Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Hydration Shells
Hydration shells are layers of water molecules that surround ions when they dissolve in water. The polar nature of water molecules allows them to interact with charged ions, forming a structured arrangement where the oxygen atoms (partially negative) orient towards cations, while the hydrogen atoms (partially positive) face anions. This interaction stabilizes the ions in solution and is crucial for understanding solubility and ionic interactions in aqueous environments.
Recommended video:
Electron Orbitals & Energy Shells
Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds, such as potassium chloride (KCl), consist of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions held together by electrostatic forces. When dissolved in water, these compounds dissociate into their constituent ions, allowing them to interact with water molecules. Understanding the nature of ionic bonds and the behavior of ions in solution is essential for visualizing the formation of hydration shells.
Recommended video:
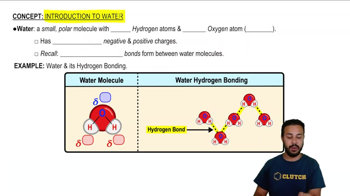
Polarity of Water
Water is a polar molecule, meaning it has a partial positive charge on one side (due to hydrogen atoms) and a partial negative charge on the other side (due to the oxygen atom). This polarity enables water to effectively interact with and stabilize ions in solution, leading to the formation of hydration shells. Recognizing the significance of water's polarity is fundamental for understanding how it facilitates the dissolution of ionic compounds.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


 5:19m
5:19m