Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Epithelial Tissue Classification
Epithelial tissues are classified based on two main criteria: cell shape and the number of cell layers. The cell shapes can be squamous (flat), cuboidal (cube-shaped), or columnar (tall and column-like), while the layers can be simple (one layer) or stratified (multiple layers). This classification helps in understanding the function and location of different epithelial types in the body.
Recommended video:
Functions of Epithelial Tissue
Cell Shape
The shape of epithelial cells is crucial for their function. Squamous cells facilitate diffusion and filtration due to their thinness, cuboidal cells are involved in secretion and absorption, and columnar cells often contain microvilli or cilia, enhancing absorption and movement of substances. Understanding these shapes aids in identifying the specific roles of various epithelial tissues.
Recommended video:
Forces That Shape the Lungs
Number of Cell Layers
The number of cell layers in epithelial tissue affects its protective capabilities and functional properties. Simple epithelium allows for efficient exchange of materials, while stratified epithelium provides a barrier against mechanical stress and pathogens. This distinction is essential for recognizing how different epithelial types contribute to overall tissue function and health.
Recommended video:
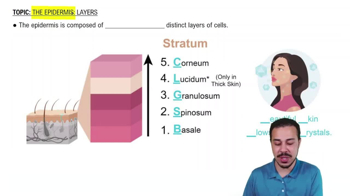
Introduction to Layers of the Epidermis
 Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 3:40m
3:40m
