Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
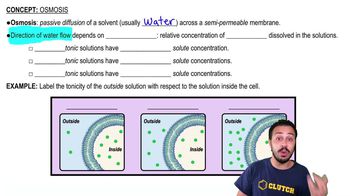
Osmosis
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration. In the context of a cell in salty seawater, osmosis explains how water will move out of the cell to balance the higher concentration of solutes (salt) outside the cell, leading to cell shrinkage.
Recommended video:
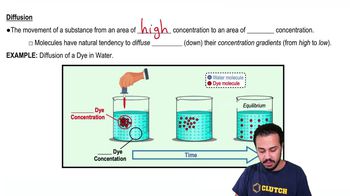
Diffusion
Diffusion is the process by which molecules spread from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. In the case of a cell in salty seawater, sodium and chloride ions may diffuse into the cell if the concentration of these ions is lower inside the cell compared to the surrounding seawater, although this is not the primary effect in this scenario.
Recommended video:
Active Transport
Active transport is the movement of ions or molecules across a cell membrane against their concentration gradient, requiring energy, usually in the form of ATP. While active transport is crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis, in the context of a cell in salty seawater, it is not the primary mechanism at play for water movement, which is primarily driven by osmosis.
Recommended video: