Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Proto-oncogenes
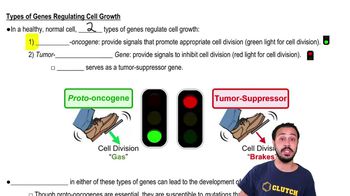
Proto-oncogenes are normal genes that play a crucial role in regulating cell growth and division. They encode proteins that help control the cell cycle, promote cell survival, and facilitate normal cellular functions. When mutated or overexpressed, these genes can become oncogenes, leading to uncontrolled cell proliferation and cancer.
Recommended video:
Types of Genes Regulating Cell Growth
Oncogenes
Oncogenes are mutated forms of proto-oncogenes that contribute to the development of cancer. They can arise from various mechanisms, including point mutations, gene amplifications, or chromosomal rearrangements. The activation of oncogenes leads to the promotion of excessive cell division and survival, overriding the normal regulatory mechanisms of the cell.
Recommended video:
Types of Genes Regulating Cell Growth
Cell Cycle Regulation
Cell cycle regulation is a complex process that ensures cells divide at the right time and in a controlled manner. Key proteins, including those encoded by proto-oncogenes, are involved in checkpoints that monitor the cell's readiness to proceed through the cycle. Disruption of this regulation, often due to mutations in proto-oncogenes, can result in cancerous growth.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance