Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Na+/K+ Pump
The Na+/K+ pump is a vital membrane protein that actively transports sodium (Na+) out of the cell and potassium (K+) into the cell, using ATP for energy. This process is essential for maintaining the electrochemical gradient across the cell membrane, which is crucial for various cellular functions, including the generation of action potentials in neurons.
Recommended video:
Primary Active Transport: Na+/K+ Pump
Gated Channels
Gated channels are specialized protein structures in the cell membrane that open or close in response to specific stimuli, allowing ions to flow in or out of the cell. These channels play a critical role in the initiation and propagation of action potentials by enabling rapid changes in membrane potential when ions like Na+ and K+ move across the membrane.
Recommended video:
Anastomoses Form Collateral Channels
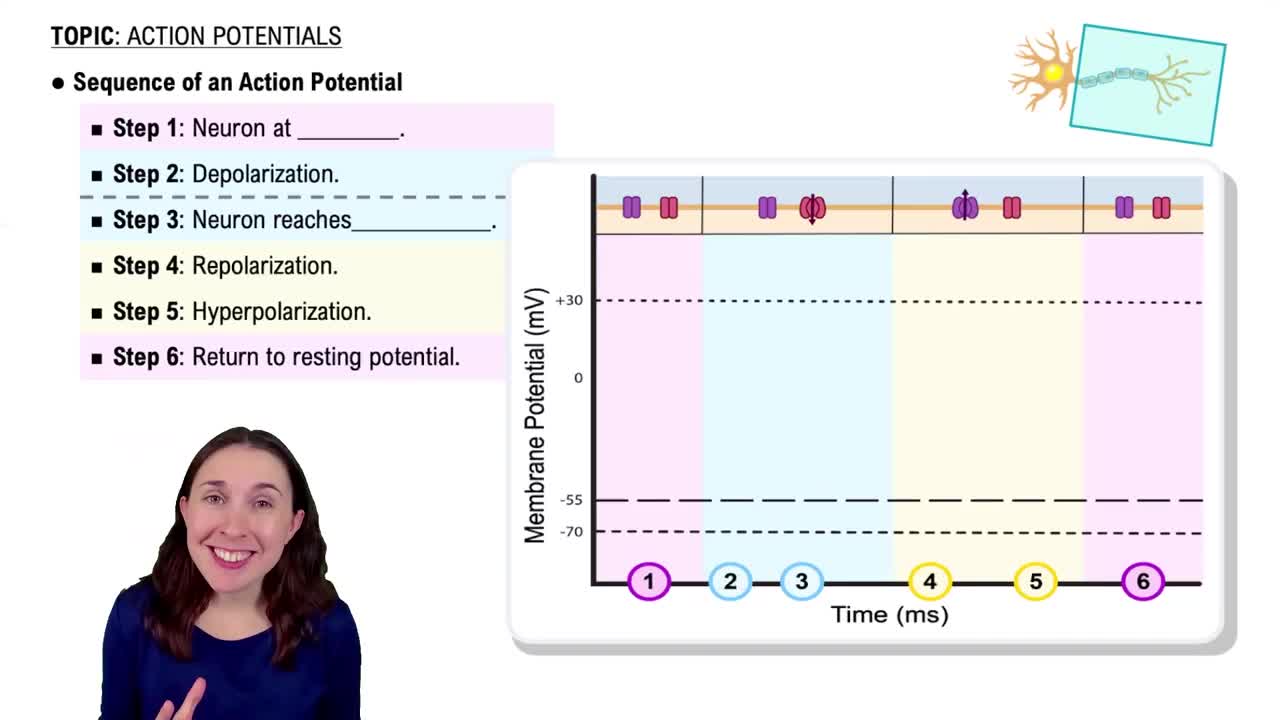
Action Potential
An action potential is a rapid, temporary change in the electrical membrane potential of a neuron or muscle cell, allowing for the transmission of signals. It occurs when the membrane depolarizes due to the influx of Na+ through gated channels, followed by repolarization as K+ exits the cell, restoring the resting membrane potential and enabling further signaling.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

 7:53m
7:53m