Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Adaptation
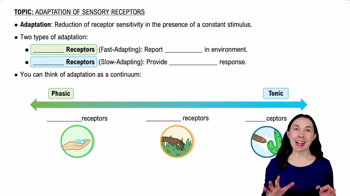
Adaptation refers to the process by which sensory receptors become less sensitive to constant stimuli over time. This phenomenon allows organisms to focus on changes in their environment rather than being overwhelmed by unchanging stimuli. For example, when you enter a room with a strong odor, you may initially notice it, but after a while, you become less aware of it as your sensory receptors adapt.
Recommended video:
Transduction
Transduction is the process by which sensory stimuli are converted into electrical signals that can be interpreted by the nervous system. This process is essential for all sensory modalities, as it allows the brain to understand and respond to various forms of stimuli, such as light, sound, and touch. For instance, in vision, light is transduced by photoreceptors in the retina into neural signals.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Sensory Receptors Example 1
Sensory Coding
Sensory coding is the way in which sensory information is represented in the nervous system. It involves the transformation of physical stimuli into a format that the brain can interpret, often through patterns of neural firing. Different sensory modalities have distinct coding strategies, such as frequency coding in hearing or spatial coding in vision, which help the brain process and understand complex sensory information.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution