Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Mitosis
Mitosis is a type of cell division that results in two genetically identical daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the original cell. In humans, somatic cells undergo mitosis to maintain the diploid number of chromosomes, which is 46. This process is crucial for growth, repair, and asexual reproduction.
Recommended video:
Chromosome Number
Chromosome number refers to the total count of chromosomes in a cell. In humans, somatic cells have 46 chromosomes, organized into 23 pairs. During mitosis, the chromosome number remains constant, meaning that each daughter cell will also have 46 chromosomes, ensuring genetic continuity.
Recommended video:
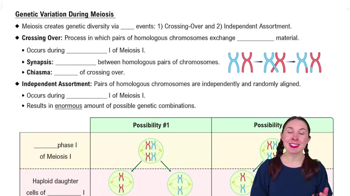
Genetic Variation During Meiosis
Daughter Cells
Daughter cells are the two new cells that result from the division of a parent cell during mitosis. Each daughter cell inherits an identical set of chromosomes from the parent cell, maintaining the same chromosome number. This is essential for the proper functioning and genetic stability of tissues in multicellular organisms.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Cell Division
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


 9:40m
9:40m