Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is a complex network of proteins and carbohydrates that provides structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells. It plays a crucial role in tissue and organ function, influencing cell behavior, migration, and differentiation. Understanding the ECM is essential for grasping how cells interact with their environment and maintain tissue integrity.
Recommended video:
Glycoproteins
Glycoproteins are proteins that have carbohydrate chains attached to them, which can influence their function and interactions. In the context of the ECM, glycoproteins serve as cell-adhesion molecules, facilitating the binding of cells to the matrix and to each other. This adhesion is vital for maintaining tissue structure and enabling communication between cells.
Recommended video:
Unicellular Exocrine Glands - Goblet Cells
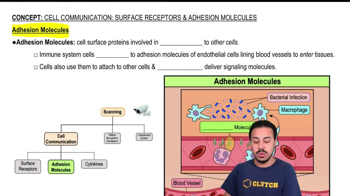
Cell-Adhesion Molecules (CAMs)
Cell-adhesion molecules (CAMs) are a group of proteins located on the cell surface that mediate the attachment between cells and the ECM or other cells. They play a critical role in various biological processes, including tissue formation, immune response, and wound healing. Understanding CAMs is key to comprehending how cells maintain their organization and respond to their environment.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 0:48m
0:48m