Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lymphoid Organs and Tissues
Lymphoid organs and tissues, such as the spleen, thymus, and lymph nodes, are crucial components of the immune system. They serve as sites for the production and maturation of lymphocytes, which are essential white blood cells involved in immune responses. These organs also facilitate the trapping and filtering of pathogens, thereby playing a vital role in the body's defense mechanisms.
Recommended video:
Immune System Function
The immune system is responsible for identifying and eliminating pathogens, such as bacteria and viruses, that invade the body. It comprises various cells, including lymphocytes, macrophages, and antibodies, which work together to recognize and destroy foreign invaders. Understanding how lymphoid organs contribute to this process is essential for grasping the overall function of the immune system.
Recommended video:
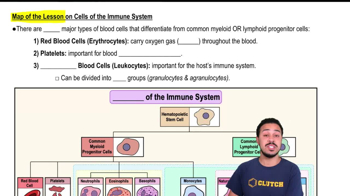
Map of the Lesson on Cells of the Immune System
Surface Barriers of the Immune System
Surface barriers, such as the skin and mucous membranes, are the first line of defense in the immune system. They act as physical and chemical barriers to prevent pathogens from entering the body. Unlike lymphoid organs, which are involved in the immune response after a pathogen has breached these barriers, surface barriers do not originate from lymphoid tissues, making this distinction important in understanding the immune system's structure and function.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution

 4:36m
4:36m