Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Endosymbiotic Theory
The endosymbiotic theory posits that certain organelles, specifically mitochondria and plastids, originated from free-living prokaryotes that were engulfed by ancestral eukaryotic cells. This theory explains how these organelles have their own DNA and replicate independently, supporting the idea that they were once separate organisms that formed a symbiotic relationship with host cells.
Recommended video:
Mitochondria vs. Plastids
Mitochondria are organelles responsible for energy production through cellular respiration, while plastids, such as chloroplasts, are involved in photosynthesis. The presence of mitochondria in all eukaryotes suggests a fundamental role in energy metabolism, whereas plastids are only found in specific groups, indicating a later evolutionary development linked to photosynthesis.
Recommended video:
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is distinct from nuclear DNA and is inherited maternally. It is more similar to prokaryotic DNA than to nuclear DNA, supporting the idea that mitochondria originated from prokaryotic ancestors. This genetic evidence is crucial for understanding the evolutionary history of eukaryotic cells and their organelles.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance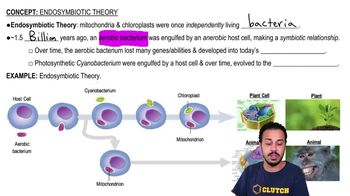



 6:58m
6:58m