Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
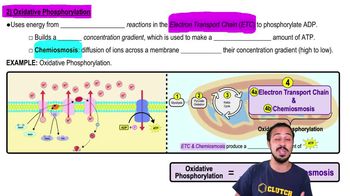
The electron transport chain is a series of protein complexes and other molecules located in the inner mitochondrial membrane. It plays a crucial role in cellular respiration by transferring electrons from electron donors like NADH and FADH2 to electron acceptors, ultimately producing ATP through oxidative phosphorylation.
Recommended video:
Proton Gradient
As electrons are transferred through the ETC, protons (H+) are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space, creating a proton gradient. This gradient is essential for ATP synthesis, as protons flow back into the matrix through ATP synthase, driving the conversion of ADP to ATP.
Recommended video:
Concentration Gradients and Diffusion
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation is the process by which ATP is produced using the energy derived from the electron transport chain. It involves the coupling of electron transport to ATP synthesis, where the energy released from electron transfers is harnessed to phosphorylate ADP, forming ATP, which is the primary energy currency of the cell.
Recommended video:
Oxidative Phosphorylation