Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Cell Membrane Structure
The cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer that serves as a barrier to most substances. It is selectively permeable, allowing certain molecules to pass while restricting others. Small, nonpolar molecules like oxygen and carbon dioxide can diffuse freely, while larger or charged molecules require assistance from membrane proteins.
Recommended video:
Membrane Proteins
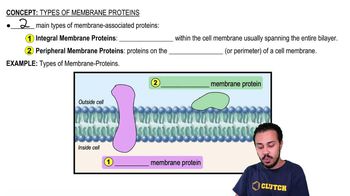
Membrane proteins are integral or peripheral proteins that facilitate the transport of substances across the cell membrane. They play crucial roles in transporting ions and larger polar molecules that cannot pass through the lipid bilayer directly. These proteins can function as channels or carriers, enabling the movement of charged molecules and other substances.
Recommended video:
Types of Membrane Proteins
Diffusion and Osmosis
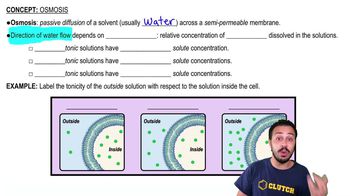
Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, while osmosis specifically refers to the diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane. Both processes are passive and do not require energy. However, charged molecules cannot diffuse freely and typically need membrane proteins to facilitate their movement.
Recommended video: